Have you ever opened your car hood and ever wondered what's going on in there? A car engine can look like a big confusing piece of metal, tubes, and wires, all put in together.
You might wanna know the mechanism of the engine, due to curiosity or maybe it's in your syllabus. You also wanted to know "2 liters in-line engine", "twin-turbocharged", "supercharged engine", etc. So, what does that mean?
Here you will get all your answers. First, we will see the definitions, and then we'll study it in deep.
DEFINITION:-
The engine is the powerhouse of a car. The chemical energy of the fuel is converted in thermal energy, and this thermal energy is converted in mechanical energy which is then supplied to the transmission system. In the end, the reciprocating motion is converted into rotary motion.
PARTS:-
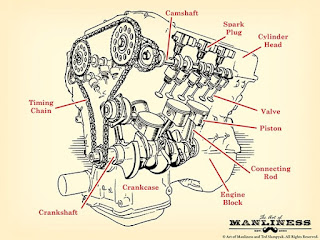
1. Spark Plug
2. Valves
3. Piston
4. Piston Rings
5. Connecting Rod
6. Crankshaft
7. Camshaft
8. Timing belt
9. Sump
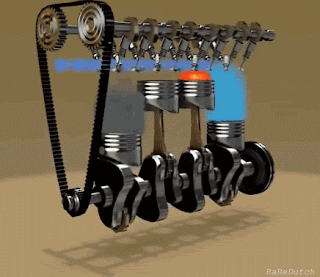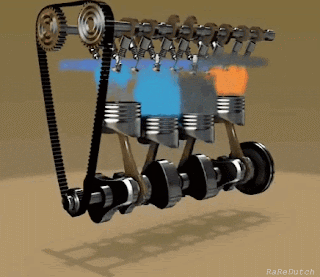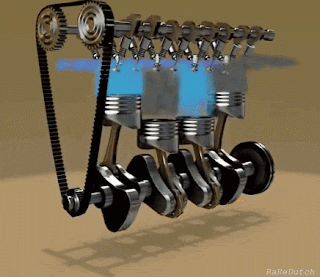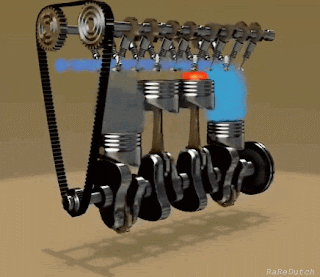
The basic concept of an engine is to reciprocate the piston into cylinders. The piston-cylinder arrangement may vary according to the requirements, space available, etc.
Let's have a look at some key parts of an engine:-
SPARK PLUG:-
The spark plug supplies the spark at the end of the combustion process due to which the air-fuel mixture burns and power stroke is performed. The supply of spark must be on time so that engine works properly. In C.I. Engines (Diesel Engine), the spark plug is absent. In a diesel engine, the combustion takes place with the help of compressed air. The air-fuel mixture is compressed up to a point until it becomes very hot.
VALVES:-
There are 2 valves namely inlet and outlet. The intel valve allows the air-fuel mixture to enter the cylinder during suction stroke. And the outlet valve allows the exhaust to flow out during exhaust stroke. Both the valves are operated with the help of a camshaft. And both are kept closed during combustion stroke.
PISTON:-
A piston is a cylindrical piece of metal that moves up and down while performing the strokes.
PISTON RINGS:-
There are three types of piston ring, compression ring, scrapper ring, and oil ring. The piston ring provides a seal between the outer edge of the piston and the inner edge of the cylinder. It serves two purposes:-
- It prevents the air-fuel mixture and the exhaust from leaking into the sump during compression and combustion.
- It prevents the oil to enter into the cylinder from the sump.
CONNECTING ROD:-
The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft. It can rotate in both the end so that it can adjust itself while the piston reciprocates.
CRANKSHAFT:-
It's a rotating shaft which converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotating motion. The piston is connected to the crankshaft with the help of a connecting rod. The crankshaft is also connected to the camshaft with the help of a timing chain (similar to the bicycle chain).
CAMSHAFT:-
A camshaft is used to operate the valves. The timing gear is used to operate the camshaft. The timing gear connects the crankshaft and the camshaft.
TIMING BELT:-
The timing belt, timing chain, or cambelt is mainly used to synchronize the rotational motion between the camshaft and the crankshaft so the valves open and closes on proper time during each cylinder's intake and exhaust stroke.
OIL SUMP:-
A sump is also called as an oil reservoir, oil pan, or oil tray. It is used to store the oil which is later used by the engine.
Labeled diagram of S.I. Engine
WHAT IS A FOUR-STROKE AND TWO-STROKE IN AN ENGINE?
FOUR-STOKE:-
The 4 strokes of an engine are Suction, Compression, Combustion, and Exhaust. The strokes are completed in 2 revolutions.
- In a first stroke, the piston moves from the top dead center (TDC) to the bottom dead center (BDC) creating a vacuum inside the cylinder due to which the air-fuel mixture enters the cylinder.
- After a suction stroke, a compression stroke is performed in which the piston travels from BDC to TDC, in which the air-fuel mixture is compressed.
- At the end of the compression, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture which leads to the burning of the mixture due to which the piston experiences an extreme downward force, hence it is called Power Stroke.
- The fourth stroke that is the exhaust stroke is performed to remove the burnt mixture out of the cylinder. In this, the piston travels from BDC to TDC.
TWO-STROKE:-
In a two-stroke engine, the strokes are completed in one revolution. Overall it contains 2 processes:-
- Compression Stroke:- The inlet port opens, the air-fuel mixture enters the chamber, and the piston moves u hence compressing the mixture. A spark plug ignites the mixture and power stoke begins.
- Power stroke:- The heated gas exerts high pressure on the cylinder, hence pushing the cylinder downwards and the burnt gas is eliminated from the chamber.
C.I. ENGINE:-
The main difference between S.I Engine and C.I. engine is that in C.I. Engine Spark Plug is absent. The C.I. Engine also operates on four-stroke. All the strokes are the same. But during suction stroke, the air-fuel mixture doesn't enter into the chamber instead of which only air enters. The air is then compressed, at some point, the temperature of the air reaches its self-ignition point during which the diesel is spread with the help of a fuel injector. Hence the air and diesel burns and power stroke is performed. Then the burnt fuel is removed out of the engine during the exhaust stroke.
 |
Strokes of C.I. Engine |
COMPARISON BETWEEN S.I. ENGINES AND C.I. ENGINES:-
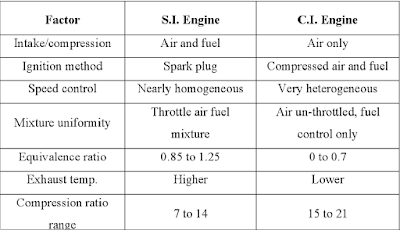 |
Comparison between S.I. Engines and C.I. Engines |
-A BLOG BY AMAAN ATTAR
PART 2 WILL BE OUT ON 25TH AUGUST 2020.
THANKS FOR READING, DO SUBSCRIBE TO MY BLOG FOR MORE SUCH CONTENTS AND ALSO CHECKOUT MY INSTAGRAM PAGE BY CLICKING ON THE LINK BELOW:-
FOR ANY SUGGESTIONS FEEL FREE TO EMAIL ME:-








2 Comments